Hydrosensing has published a new article “Roles of Hormones in Regulating Root Growth-Water Interactions” on Journal of Experimental Botany.
Summary
Water stress is a major threat to agriculture, with drought alone causing significant crop losses. Roots play a crucial role in helping plants cope by detecting changes in soil moisture and triggering adaptive responses. These responses occur at multiple levels—morphological, anatomical, and biochemical—to help plants manage both severe drought and subtle variations in soil water availability.
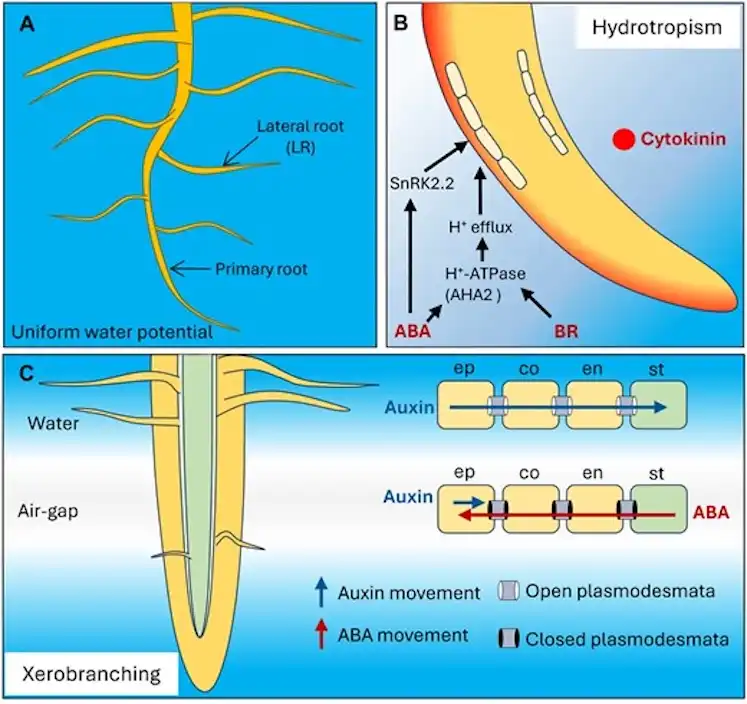
Key root behaviors include hydrotropism (growing toward moisture), xerobranching (suppressing root formation in dry soil), and hydropatterning (adjusting root growth based on localized water availability). These adaptations are regulated by complex hormonal signaling networks at the cellular level.
Recent research has shed light on the sophisticated mechanisms behind these root responses. Understanding and harnessing these processes could help develop crops with enhanced resilience to water stress, improving agricultural sustainability in a changing climate.
Full reference: Sharma, S., Bennett, M. J., & Mehra, P. (2025). Roles of Hormones in Regulating Root Growth-Water Interactions. Journal of Experimental Botany, eraf063 https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraf063
Image: graphical abstract. Credit: Current Biology.